
- ANDROID ACCESSIBILITY SCREEN READER HOW TO
- ANDROID ACCESSIBILITY SCREEN READER ANDROID
- ANDROID ACCESSIBILITY SCREEN READER DOWNLOAD

Navigation in the app is not strictly left-to-right and top-to-bottom.
To open the tutorial again in the future, navigate to Settings > Accessibility > TalkBack > Settings > Launch TalkBack tutorial. It may be helpful to navigate the tutorial with your eyes closed.

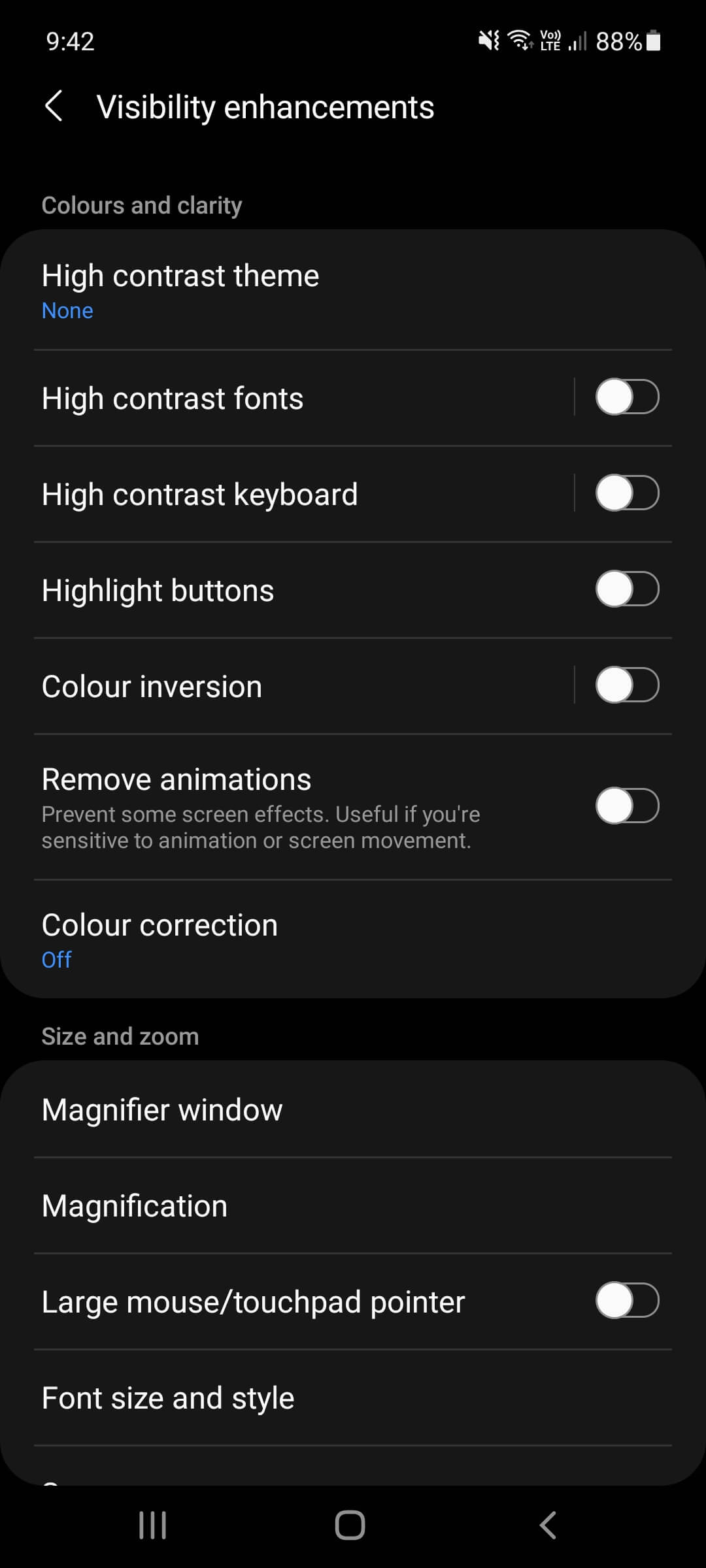
The currently selected item has a green border around the view. Swipe left or right to explore the items in tab (focus) order. You can touch items individually or move your finger over the screen.
ANDROID ACCESSIBILITY SCREEN READER ANDROID
ANDROID ACCESSIBILITY SCREEN READER DOWNLOAD
To test TalkBack on the emulator or on a device without TalkBack, download and build the source. The source for the TalkBack feature is available on GitHub. Note: By default, TalkBack is unavailable in the Android emulator and in some older devices.
ANDROID ACCESSIBILITY SCREEN READER HOW TO
In this task, you enable TalkBack to understand how screen readers work and how to navigate apps. Users with visual impairments might rely on TalkBack to use your app. With TalkBack enabled, the user can interact with their Android device without seeing the screen, because Android describes screen elements aloud. TalkBack is Android's built-in screen reader. Experiment with the various accessibility settings on an Android device.įor this lesson you use the built-in Android settings and apps.Enable other accessibility settings to customize your device.Turn on TalkBack and navigate the Google user interface with TalkBack enabled.Your device or version of Android may not have all these options, or the options may have different names. Note: This practical describes the accessibility features in Android 7 (Nougat). In this lesson, you explore the features Android provides on the device to enable accessibility, including Google TalkBack (Android's screen reader) and other options in the Android framework. When you develop your apps with accessibility in mind, you make the user experience better not only for users with these disabilities, but also for all of your other users. Explore TalkBack and text-to-speechĪndroid apps should be usable by everyone, including people with disabilities.Ĭommon disabilities that can affect a person's use of an Android device include blindness, low vision, color blindness, deafness or hearing loss, and restricted motor skills. The practical workbook for the Advanced Android Development course is now available as Unit 6: Working with Architecture Componentsġ4.1B: Deleting and updating data with Room 3.2: Working with sensor-based orientationĤ.1A: Using the Profile GPU Rendering toolĤ.1B: Using the Debug GPU Overdraw and Layout Inspector toolsĤ.1C: Using the Systrace and dumpsys toolsĤ.3: Optimizing network, battery, and image useĥ.2: Using the locale to format informationġ0.1A: Creating a custom view from a View subclassġ0.1B: Creating a custom view from scratchġ1.1C: Applying clipping to a Canvas object


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
